Curiosity Navigation Curiosity Home Mission Overview Where is Curiosity? Mission Updates Science Overview Instruments Highlights Exploration Goals News and Features Multimedia Curiosity Raw Images Images Videos Audio More Resources Mars Missions Mars Sample Return Mars Perseverance Rover Mars Curiosity Rover MAVEN Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Mars Odyssey More Mars Missions The Solar System The Sun Mercury Venus Earth The Moon Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto & Dwarf Planets Asteroids, Comets & Meteors The Kuiper Belt The Oort Cloud 3 min read
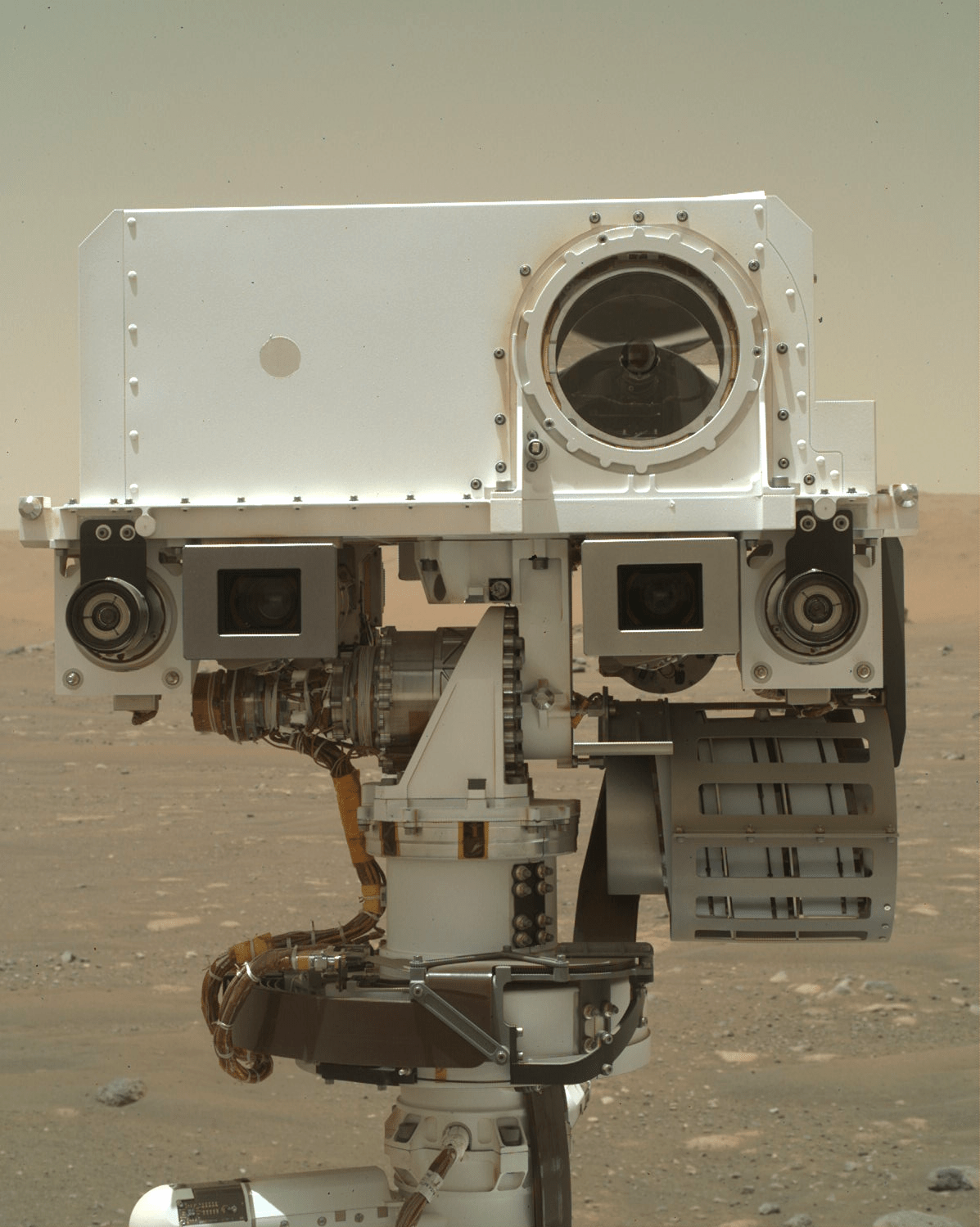
Sols 4329-4330: Continuing Downhill  A post-drive image from NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity showcases the rover’s two front wheels. The right front wheel is parked on top of a rock, which altered the science team’s plan for the day. This image was taken by the Front Hazard Avoidance Camera (Front Hazcam) aboard Curiosity on sol 4328 — Martian day 4,328 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission — on Oct. 9, 2024, at 02:30:55 UTC. NASA/JPL-Caltech Earth planning date: Wednesday, Oct. 9, 2024
A post-drive image from NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity showcases the rover’s two front wheels. The right front wheel is parked on top of a rock, which altered the science team’s plan for the day. This image was taken by the Front Hazard Avoidance Camera (Front Hazcam) aboard Curiosity on sol 4328 — Martian day 4,328 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission — on Oct. 9, 2024, at 02:30:55 UTC. NASA/JPL-Caltech Earth planning date: Wednesday, Oct. 9, 2024
Curiosity is continuing to make good progress downhill along the western edge of the Gediz Vallis channel, allowing us to take another look from a different perspective at this area we’ve spent many months exploring. The drive from Monday’s plan executed as expected, positioning us about 30 meters (about 98 feet) north of our last location. Unfortunately, the rover parked with its right front wheel atop an unstable-looking rock, so we decided to keep the arm stowed rather than risk having the wheel slip with the arm unstowed.
As a consequence, our plan today is all remote sensing, kicking off with a LIBS activity on a bedrock target “Sapphire Lake” and long distance RMI mosaics of “Pinnacle Ridge,” which avid readers may remember was a focus of an imaging campaign while we were still in the channel. Mastcam gets its turn on both Sapphire Lake and Pinnacle Ridge, as well as a Mastcam-exclusive target, “Wuksachi,” to document some rover-disturbed regolith and a wheel-scuffed rock surface. This plan’s drive is also in the first sol, which will hopefully bring us nearly 40 meters (about 131 feet) further north, closer to our eventual exit from Gediz Vallis.
The first sol also sees a small collection of environmental science observations, including Navcam images to monitor dust and sand on the rover deck as well as a Navcam movie looking out over the northern horizon to look for clouds. We haven’t been seeing many clouds lately, but we are rapidly approaching the end of the current Mars Year, and the end of the dusty season. (The new year, numbered 38, begins Nov. 12; a Martian year is much longer than one on Earth, taking 687 Earth days to orbit the Sun.) Though the cloudy season won’t really pick up steam until February, the “noctilucent cloud season” will be taking place in December and January, which has produced some spectacular images in the past. Today’s plan also features an “UltraSPENDI,” or “Shunt Prevention ENV Navcam Drop-In.” This activity takes 18 cloud movies and dust devil movies over three hours and serves to prevent the rover’s batteries from remaining fully charged for an extended period of time, which would hurt their long-term health.
The second sol of this plan is pretty simple, featuring a Mastcam tau to measure the amount of dust in the atmosphere, a ChemCam AEGIS activity, some more Navcam deck monitoring, and a 360-degree Navcam survey for dust devils around the rover. As always, REMS, RAD, and DAN will be continuing with their usual activities.
Written by Conor Hayes, graduate student at York University
Details Last Updated Oct 11, 2024 Related Terms Blogs
Keep Exploring Discover More Topics From NASA Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and the seventh largest. It’s the only planet we know of inhabited…

Explore this collection of Mars images, videos, resources, PDFs, and toolkits. Discover valuable content designed to inform, educate, and inspire,…

Each robotic explorer sent to the Red Planet has its own unique capabilities driven by science. Many attributes of a…
Mars Exploration: Science Goals
The key to understanding the past, present or future potential for life on Mars can be found in NASA’s four…



 3 min read Sols 4327-4328: On the Road Again
3 min read Sols 4327-4328: On the Road Again
 3 min read Sols 4325-4326: (Not Quite) Dipping Our Toes in the Sand
3 min read Sols 4325-4326: (Not Quite) Dipping Our Toes in the Sand
 2 min read Perseverance Matters It is an important and exciting juncture in Mars exploration and astrobiology. This year, the…
2 min read Perseverance Matters It is an important and exciting juncture in Mars exploration and astrobiology. This year, the…
