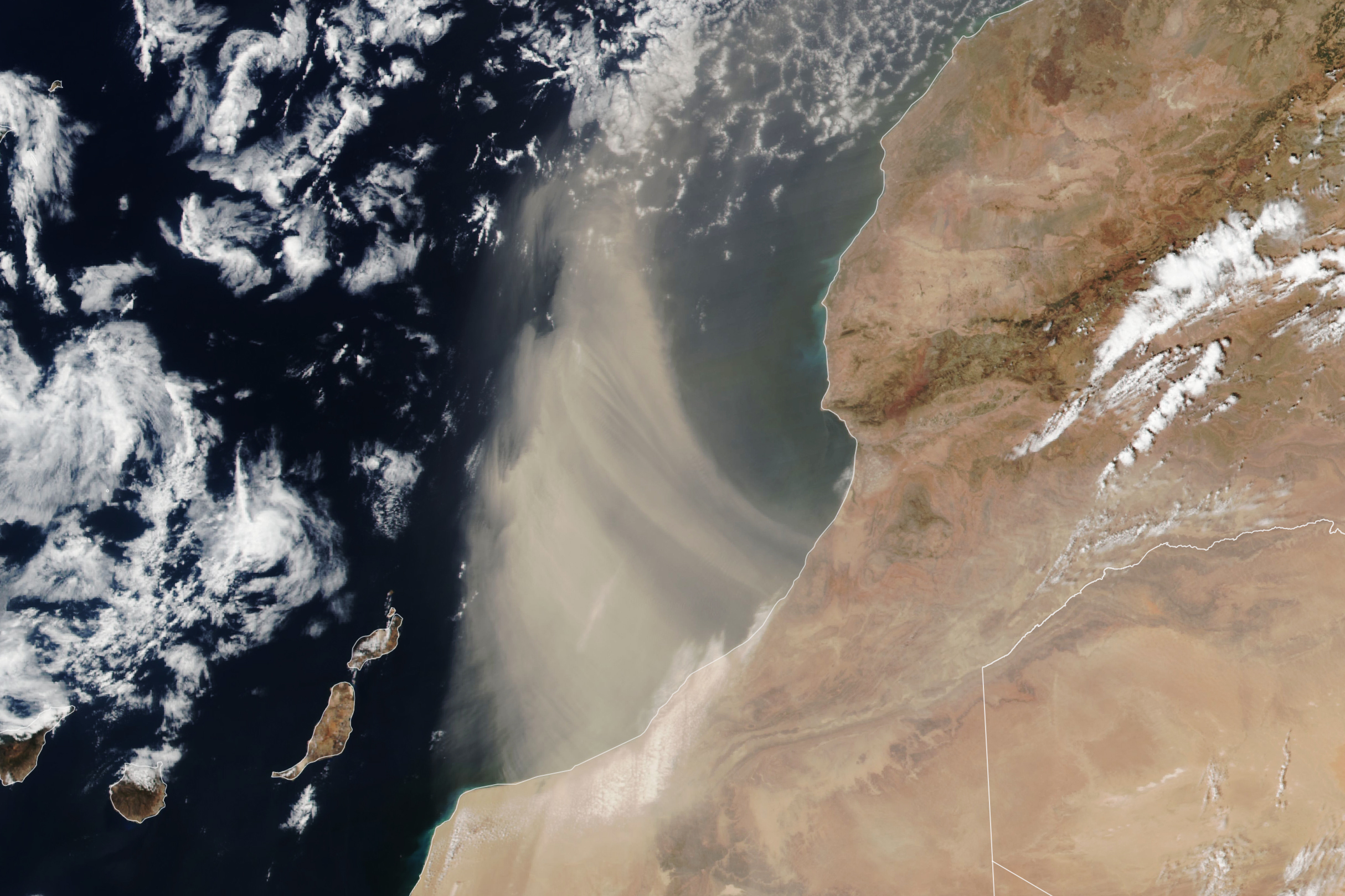
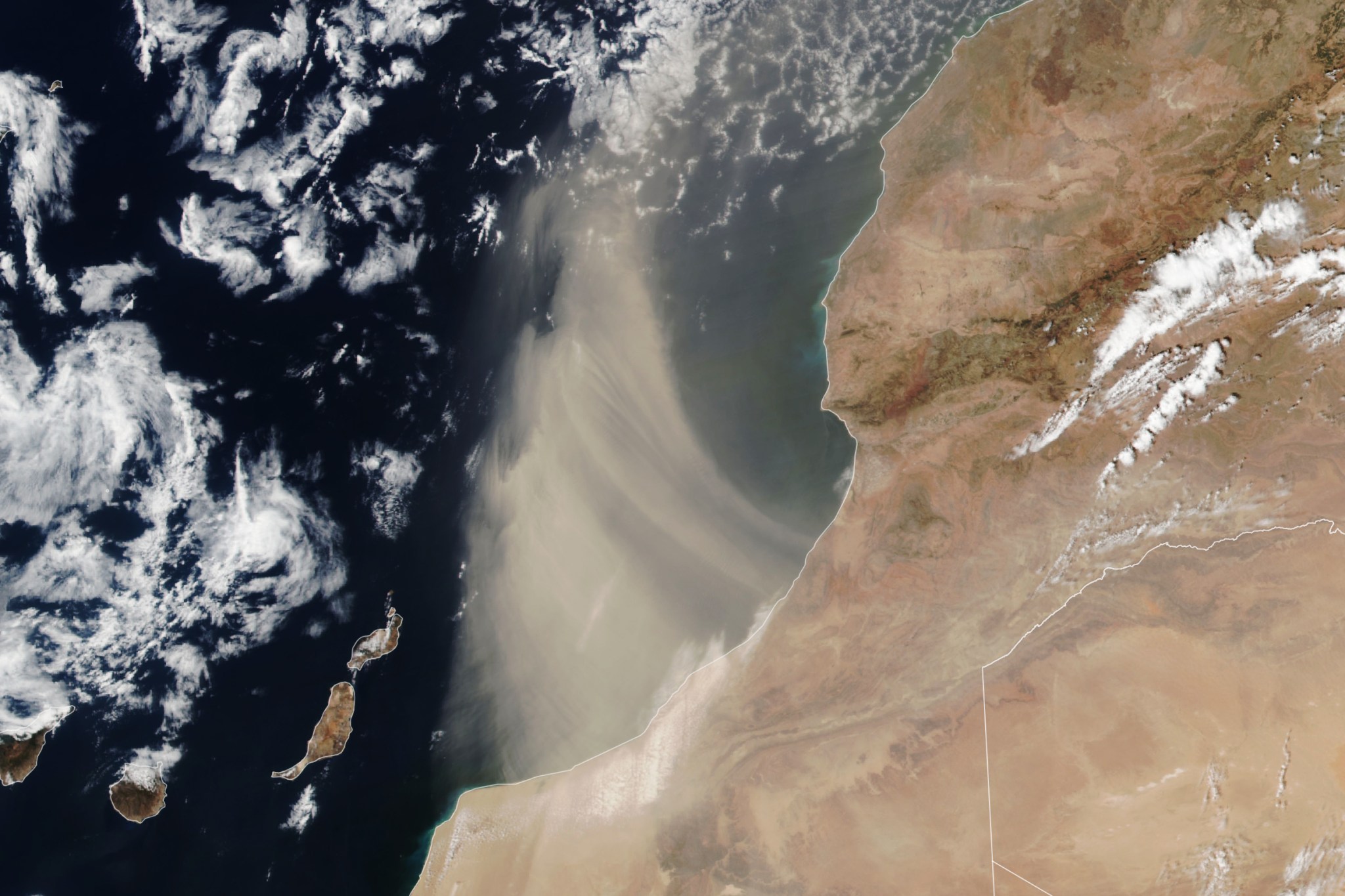
 NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using VIIRS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE, GIBS/Worldview, and the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership The Suomi NPP satellite acquired this image of a plume of Saharan dust as winds lofted it over the Atlantic Ocean on Aug. 24, 2024.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using VIIRS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE, GIBS/Worldview, and the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership The Suomi NPP satellite acquired this image of a plume of Saharan dust as winds lofted it over the Atlantic Ocean on Aug. 24, 2024.
The Sahara Desert is Earth’s largest source of airborne dust, and the particles can travel for thousands of miles. From late spring to early fall, it is common for the dry, dusty Saharan Air Layer to carry the particles westward across the Atlantic Ocean high in the atmosphere. Saharan Air Layer activity subsides after mid-August, according to NOAA, making it less likely that the plume shown here is bound for a transoceanic journey. Instead, it arcs to the north after blowing out over the ocean. Earlier in the summer, however, several clouds of fine dust from the Sahara reached the United States, creating hazy skies over Texas.
Read more about Saharan dust and why it’s interesting to scientists.
Text Credit: Lindsey Doermann
Image Credit: NASA/Lauren Dauphin, using VIIRS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE, GIBS/Worldview, and the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership