Curiosity NavigationCuriosity HomeMission OverviewWhere is Curiosity?Mission UpdatesScienceOverviewInstrumentsHighlightsExploration GoalsNews and FeaturesMultimediaCuriosity Raw ImagesImagesVideosAudioMore ResourcesMars MissionsMars Sample ReturnMars Perseverance RoverMars Curiosity RoverMAVENMars Reconnaissance OrbiterMars OdysseyMore Mars MissionsThe Solar SystemThe SunMercuryVenusEarthThe MoonMarsJupiterSaturnUranusNeptunePluto & Dwarf PlanetsAsteroids, Comets & MeteorsThe Kuiper BeltThe Oort Cloud 2 min read
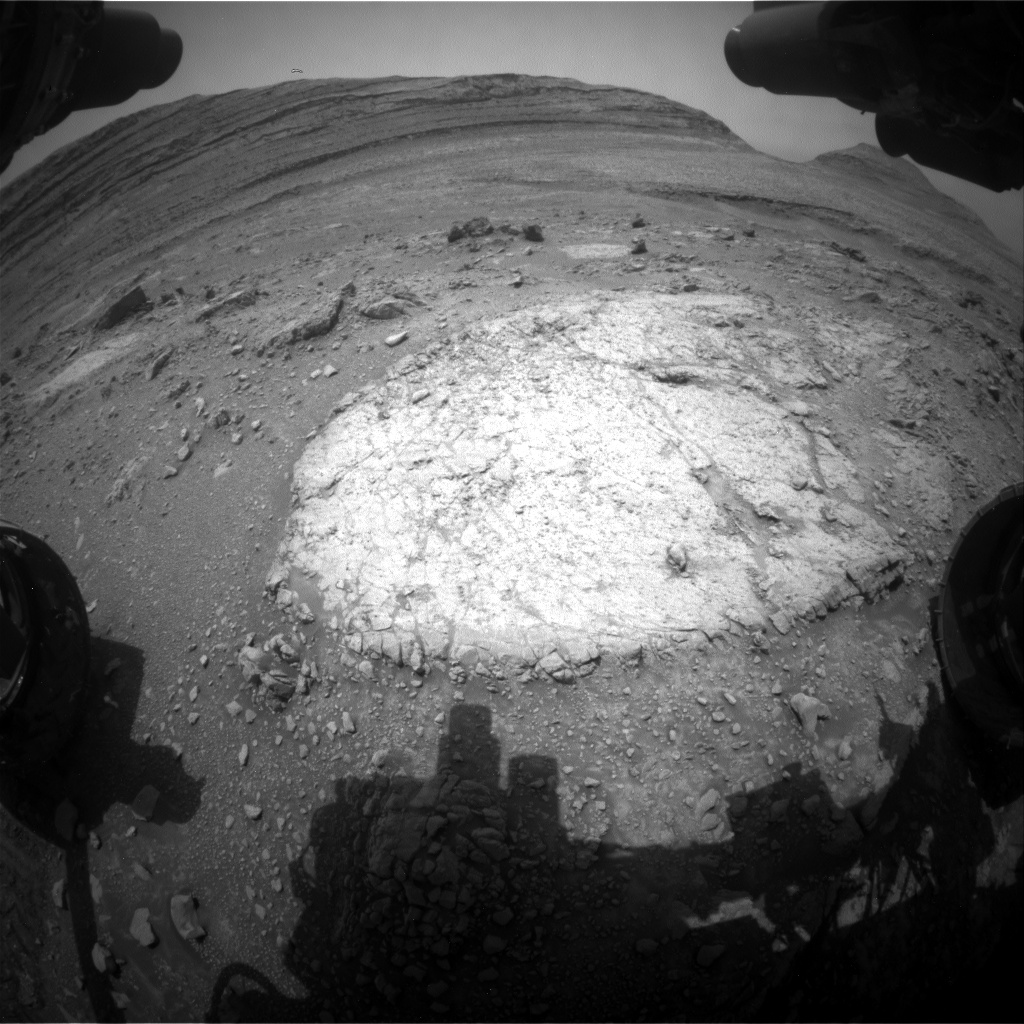
Sol 4294: Return to McDonald Pass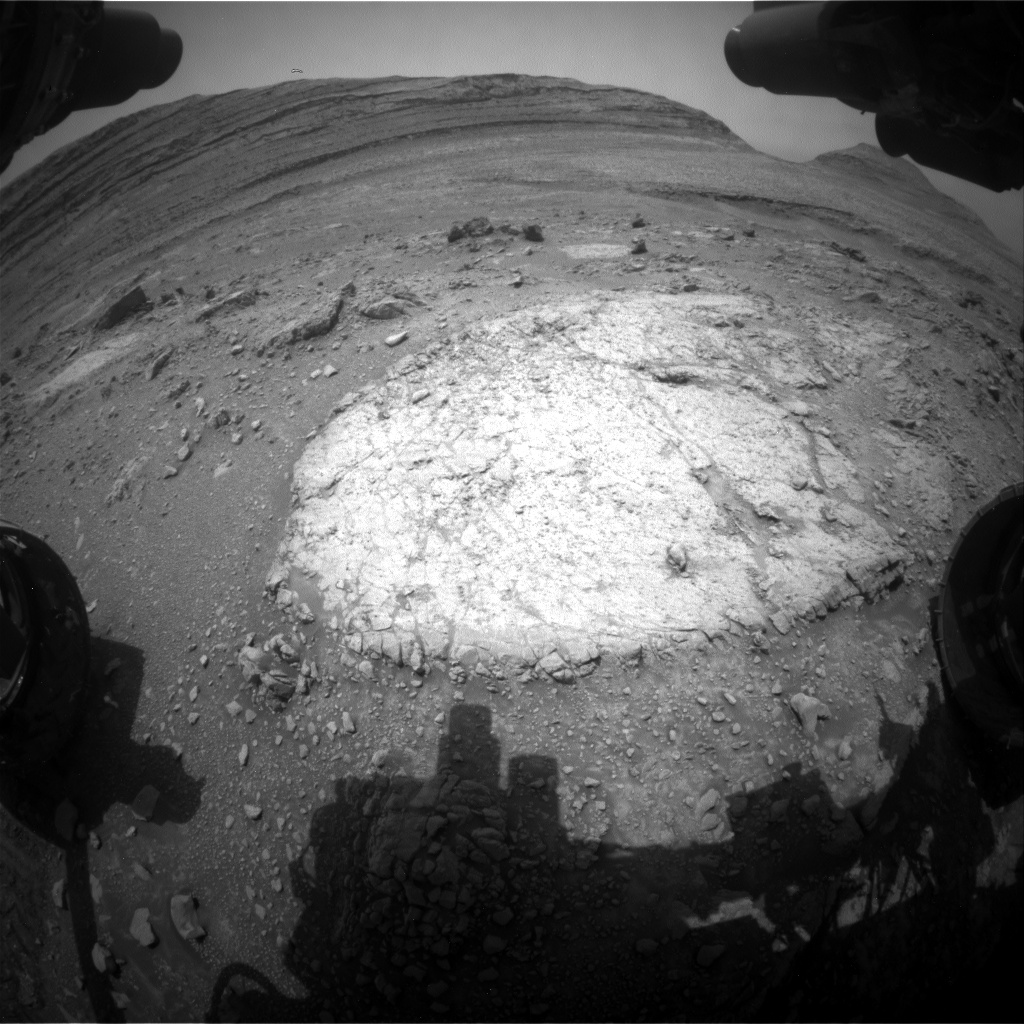  This image was taken by Front Hazard Avoidance Camera (Front Hazcam) aboard NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity on sol 4293 — Martian day 4,293 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission — Sept. 3, 2024 at 04:09:27 UTC.NASA/JPL-Caltech Earth planning date: Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024
This image was taken by Front Hazard Avoidance Camera (Front Hazcam) aboard NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity on sol 4293 — Martian day 4,293 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission — Sept. 3, 2024 at 04:09:27 UTC.NASA/JPL-Caltech Earth planning date: Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024
Curiosity has returned to “McDonald Pass,” a block within Gediz Vallis that we first spotted about a month ago (as seen in the above Front Hazcam image). The block shows some interesting zonation — the distribution of textures and colors into different areas, or zones. We’re hoping that by studying the well-exposed relationships between white, gray, and tan material at this location that we’ll be able to better understand similar relationships that we’ve observed elsewhere. The drive over the weekend got us back to McDonald Pass, but perhaps one step too far. We realized that the best spot to study these zones is directly beneath the rover, so today’s plan includes contact science and a short bump to position the rover for even more science tomorrow.
Today was a rare one-sol plan, to account for the U.S. holiday yesterday. I was on shift as the Long Term Planner and it was a fairly straightforward day once we established the best locations for contact science. The plan starts with a DRT and APXS on the central part of the slab, at a target named “Erin Lake.” Then we have a remote sensing block, which begins with some environmental monitoring to search for dust devils, measure atmospheric opacity, and monitor the movement of fines on the rover deck. The Geology Theme group planned ChemCam LIBS on the darker gray rim of this block at “Paris Lake,” along with a ChemCam passive observation on an interesting dark float block nearby. There’s also a long distance RMI mosaic to assess the yardang unit higher on Mount Sharp, and a Mastcam mosaic to evaluate the textures in a row of large clasts. Later in the afternoon, Curiosity will acquire MAHLI images of Erin Lake and another target, “Picture Puzzle,” which captures the white, gray, and tan zones. Then Curiosity will take a short drive back about 1 meter (about 3.3 feet) to position a white and gray clast in our workspace for even more contact science tomorrow.
Will McDonald Pass be the key to understanding the zonation observed in blocks throughout this region? Stay tuned!
Written by Lauren Edgar, Planetary Geologist at USGS Astrogeology Science Center
Keep Exploring Discover More Topics From NASA Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and the seventh largest. It’s the only planet we know of inhabited…



 3 min read Sols 4291-4293: Fairview Dome, the Sequel Article 33 mins ago
3 min read Sols 4291-4293: Fairview Dome, the Sequel Article 33 mins ago  3 min read Behind the Scenes at the 2024 Mars 2020 Science Team Meeting The Mars 2020 Science Team meets in Pasadena for 3 days of science synthesis
3 min read Behind the Scenes at the 2024 Mars 2020 Science Team Meeting The Mars 2020 Science Team meets in Pasadena for 3 days of science synthesis
 4 min read Sols 4289-4290: From Discovery Pinnacle to Kings Canyon and Back Again Article 7 days ago
4 min read Sols 4289-4290: From Discovery Pinnacle to Kings Canyon and Back Again Article 7 days ago